The Science of PRP and Its Hair Regrowth Potential
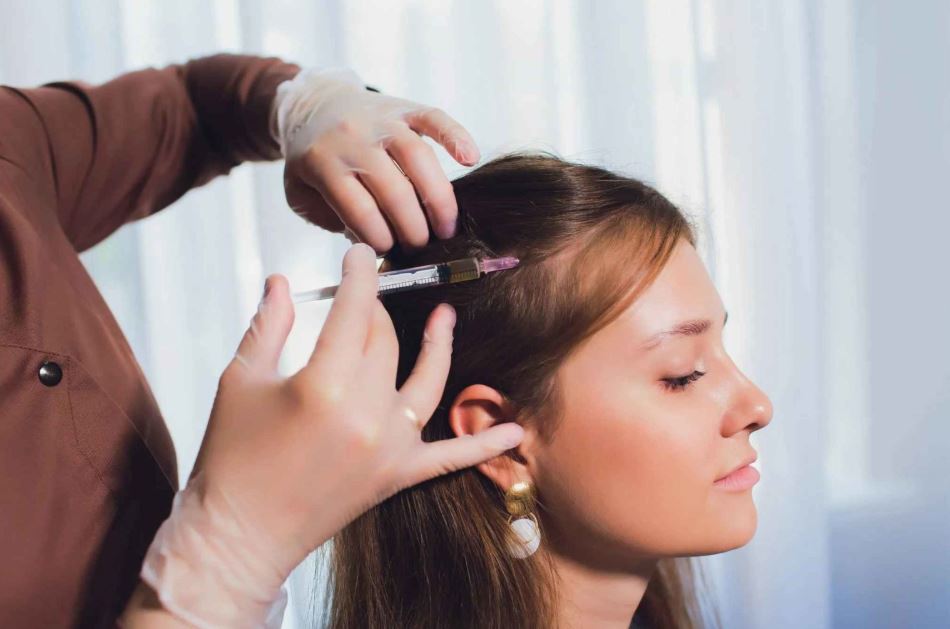
In recent years, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy has gained considerable attention as a non-surgical treatment for hair thinning and androgenic alopecia. Derived from a patient’s own blood, PRP is a concentrated form of platelets suspended in plasma, containing powerful growth factors that aid in tissue repair and regeneration. When injected into the scalp, this autologous treatment promotes healing at the cellular level, potentially reversing the miniaturization of hair follicles that leads to hair loss. In the context of hair prp therapy, the role of platelets goes far beyond simple clotting—they act as biological messengers that stimulate the proliferation of dermal papilla cells and enhance angiogenesis in the scalp.
How PRP Interacts With Hair Follicles
To understand why PRP may be effective in hair regrowth, it’s crucial to examine the biological interactions at the follicular level. Hair growth occurs in cycles: anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting). Disruptions in this cycle, often caused by hormonal imbalances, stress, genetics, or underlying medical conditions, can lead to prolonged telogen phases and follicular dormancy.
PRP reactivates dormant follicles by delivering a cocktail of growth factors like platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1). These factors promote stem cell migration, boost collagen production, and improve vascular supply to the scalp, all of which are critical for healthy hair growth. This regenerative microenvironment effectively encourages follicles to re-enter the anagen phase and supports longer, thicker hair shafts.
Platelets as Cellular Signaling Powerhouses
Platelets serve as vital components in wound healing and tissue repair, storing over 800 proteins and releasing them upon activation. When PRP is injected into the scalp, these proteins play several roles: reducing inflammation, accelerating tissue repair, and enhancing cellular metabolism. This influx of bioactive molecules initiates a cascade of reparative events that optimize conditions for follicle rejuvenation.
Among the most significant mechanisms is the upregulation of beta-catenin, a protein that influences the Wnt signaling pathway—a critical pathway in hair follicle morphogenesis and growth. Studies have shown that Wnt/β-catenin signaling is pivotal in triggering the transition from telogen to anagen. By modulating this pathway, PRP helps follicles escape dormancy and return to active growth.
Clinical Insights and Efficacy of PRP in Hair Regrowth
Multiple clinical studies have shown promising results regarding the effectiveness of PRP in treating hair loss, particularly in patients with androgenetic alopecia. A typical PRP protocol involves drawing the patient’s blood, centrifuging it to isolate the platelet-rich layer, and injecting it into targeted areas of the scalp. While variations exist in terms of frequency and volume, most patients receive treatments monthly for the first 3–4 months, followed by maintenance sessions every 4–6 months.
Patients often report noticeable improvements in hair density, texture, and overall scalp health within three to six months. However, individual responses may vary due to genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and the severity of hair loss at the time of treatment. Importantly, PRP is considered a low-risk procedure, given its autologous nature, which minimizes allergic reactions or rejection.
Despite its growing popularity, it’s worth noting that PRP is not a universal solution. Its efficacy depends largely on proper patient selection and adherence to evidence-based preparation protocols. For instance, using an optimal concentration of platelets (typically 4-5 times baseline levels) is crucial to achieving the desired therapeutic effect. Over-concentration may have diminishing returns or even counterproductive effects, emphasizing the need for medical expertise and proper technique.
Enhancing PRP Results With Adjunctive Therapies
While PRP can be a powerful standalone treatment, its efficacy is often enhanced when combined with other modalities. Microneedling, for example, creates controlled micro-injuries in the scalp that boost collagen production and improve PRP absorption. When done in conjunction with PRP, microneedling can significantly amplify growth factor delivery to the follicular units.
Additionally, combining PRP with low-level laser therapy (LLLT), minoxidil, or finasteride can further boost results. These adjunctive therapies work synergistically with PRP by promoting follicular activity, improving blood flow, and modulating hormonal influences on the scalp. Nutritional support, stress management, and regular scalp massages are also beneficial in supporting hair health holistically.
Recent advancements in regenerative medicine are exploring even more potent formulations of PRP, such as PRF (platelet-rich fibrin), which offers a slower and more sustained release of growth factors. These innovations suggest that the future of non-surgical hair restoration may involve customized, multi-layered approaches tailored to individual biology.
The Future Outlook of PRP in Hair Restoration
The continued exploration of PRP’s role in hair regrowth signals a broader shift in medical aesthetics toward minimally invasive, regenerative therapies. While traditional solutions like transplants and topical medications remain relevant, PRP introduces a biological, patient-driven approach that harnesses the body’s natural healing capacity.
Future research is expected to refine and standardize PRP protocols to optimize clinical outcomes. This includes defining ideal platelet concentrations, understanding inter-patient variability, and integrating biomarkers to predict response rates. Long-term studies are also necessary to assess the durability of PRP-induced hair regrowth and determine the best maintenance schedules.
As the field evolves, collaboration between dermatologists, researchers, and biotechnologists will be key to unlocking the full potential of PRP. With growing interest and investment in regenerative therapies, PRP may soon become a staple in comprehensive hair loss management plans, offering hope to millions experiencing hair thinning or alopecia.
Conclusion
Platelet-rich plasma therapy represents a compelling frontier in non-surgical hair restoration. Through its complex network of growth factors and regenerative capabilities, PRP targets the root causes of follicular degeneration, encouraging natural and sustained hair growth. While not a miracle cure, it holds immense promise as a scientifically grounded, patient-centered solution. Understanding its mechanisms not only empowers patients but also enables practitioners to deliver safer and more effective treatments in the battle against hair loss. Hashinvasive is at the forefront of innovative PRP hair restoration, offering tailored protocols that maximize the benefits of regenerative medicine.