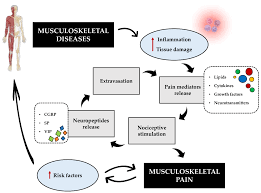
Direct acting muscle relaxants are medications that work directly on the skeletal muscles to reduce muscle tension and spasms. These drugs are often prescribed for conditions like muscle injuries, spasticity, and certain neurological disorders. They act by targeting the muscle fibers or the neuromuscular junction, leading to relaxation and pain relief. This content explains how these medications work, their types, uses, and potential side effects.
How Direct Acting Muscle Relaxants Work
Direct acting muscle relaxants target the muscles directly. They interfere with the process of muscle contraction. Muscles contract when nerve signals stimulate them. These signals cause calcium to be released inside muscle cells. Calcium triggers the interaction between actin and myosin, two proteins responsible for muscle contraction. Direct acting muscle relaxants block this process. They prevent calcium release or interfere with actin and myosin interaction. This reduces muscle tension and spasms.
Types of Direct Acting Muscle Relaxants
There are two main types of direct acting muscle relaxants: depolarizing and non-depolarizing agents. Depolarizing agents work by causing sustained muscle depolarization. This prevents further muscle contraction. Non-depolarizing agents block the receptors at the neuromuscular junction. This stops nerve signals from reaching the muscles. Both types are effective but used in different situations.
Depolarizing Agents
Depolarizing agents mimic the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. They bind to acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. This causes muscle depolarization. However, unlike acetylcholine, these agents are not quickly broken down. This leads to prolonged depolarization. Muscles cannot contract again until the agent is metabolized. Succinylcholine is a common depolarizing agent. It is often used in surgical procedures to induce muscle paralysis.
Non-Depolarizing Agents
Non-depolarizing agents block acetylcholine receptors. They prevent acetylcholine from binding to these receptors. This stops nerve signals from triggering muscle contraction. These agents are often used during surgery to maintain muscle relaxation. Examples include vecuronium and rocuronium. They are also used in critical care settings for patients on mechanical ventilation.
Uses of Direct Acting Muscle Relaxants
Direct acting muscle relaxants are used in various medical conditions. They help manage muscle spasms, spasticity, and certain neurological disorders. They are also used during surgical procedures to induce muscle paralysis.
Muscle Spasms
Muscle spasms are sudden, involuntary contractions of a muscle or group of muscles. They can be painful and limit movement. Direct acting muscle relaxants are often prescribed to relieve muscle spasms caused by injuries, overuse, or conditions like fibromyalgia. These medications help relax the muscles and reduce pain.
Spasticity
Spasticity is a condition where muscles are continuously contracted. It is often seen in neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord injuries. Direct acting muscle relaxants help reduce muscle stiffness and improve mobility in patients with spasticity.
Surgical Procedures
During surgery, muscle relaxation is often necessary. Direct acting muscle relaxants are used to induce paralysis. This allows surgeons to perform procedures without muscle interference. These medications are carefully administered and monitored to ensure patient safety.
Neurological Disorders
Certain neurological disorders cause abnormal muscle activity. Conditions like Parkinson’s disease and dystonia can lead to involuntary muscle contractions. Direct acting muscle relaxants help manage these symptoms. They improve quality of life for patients with these disorders.
Side Effects of Direct Acting Muscle Relaxants
Like all medications, direct acting muscle relaxants can cause side effects. These vary depending on the type of medication and the individual. Common side effects include muscle weakness, dizziness, and fatigue. More serious side effects can occur, especially with improper use.
Muscle Weakness
Direct acting muscle relaxants can cause generalized muscle weakness. This is because they affect all skeletal muscles, not just the ones causing spasms or stiffness. Patients may find it difficult to perform daily activities while taking these medications.
Dizziness and Fatigue
Dizziness and fatigue are common side effects. These medications can affect the central nervous system, leading to feelings of drowsiness or lightheadedness. Patients are advised to avoid driving or operating heavy machinery while taking these drugs.
Respiratory Issues
In some cases, direct-acting muscle relaxants can affect the muscles involved in breathing. This can lead to respiratory depression, especially in high doses or with prolonged use. Patients with pre-existing respiratory conditions should use these medications with caution.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to direct acting muscle relaxants are rare but possible. Symptoms may include rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Immediate medical attention is required if an allergic reaction occurs.
Precautions When Using Direct Acting Muscle Relaxants
Patients should take certain precautions when using direct acting muscle relaxants. These medications should be used only as prescribed. Overuse or misuse can lead to serious side effects. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about any pre-existing conditions or medications they are taking.
Avoid Alcohol
Alcohol can increase the sedative effects of direct acting muscle relaxants. This can lead to excessive drowsiness or dizziness. Patients should avoid alcohol while taking these medications.
Monitor for Side Effects
Patients should monitor for side effects and report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider. This includes muscle weakness, difficulty breathing, or signs of an allergic reaction.
Use in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The safety of direct acting muscle relaxants during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well established. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before using these medications.
Drug Interactions
Direct acting muscle relaxants can interact with other medications. This includes sedatives, opioids, and certain antibiotics. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Conclusion
Direct acting muscle relaxants are effective medications for managing muscle spasms, spasticity, and certain neurological disorders. They work by directly targeting the muscles or the neuromuscular junction. These medications are also used during surgical procedures to induce muscle paralysis. While they are generally safe, they can cause side effects like muscle weakness, dizziness, and respiratory issues. Patients should use these medications as prescribed and take necessary precautions. Understanding how these drugs work and their potential risks can help patients use them safely and effectively.