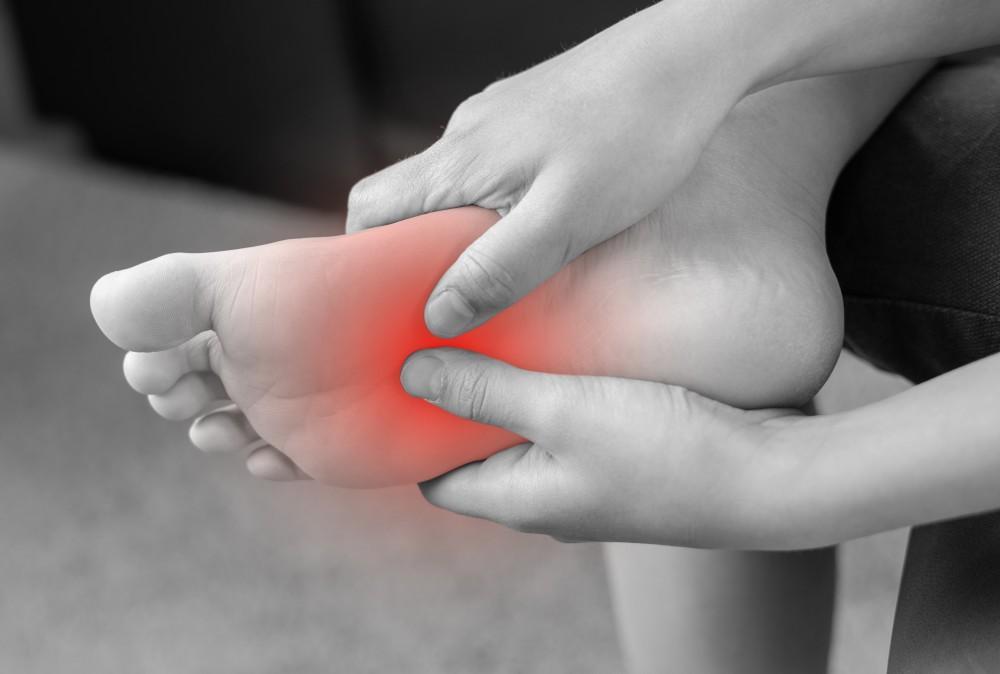
Neuropathic pain is a complex and often debilitating condition that arises from damage to the nervous system. Unlike nociceptive pain, which is caused by injury or inflammation, neuropathic pain results from dysfunction in the nervous system itself. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments for pain, including the role of pregabalin, a commonly prescribed medication for this condition.
1. Causes of Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
-
Diabetes: One of the most common causes of neuropathic pain is diabetic neuropathy, which occurs due to prolonged high blood sugar levels damaging the nerves, particularly in the extremities.
-
Injuries: Physical injuries, such as fractures, spinal cord injuries, or traumatic brain injuries, can lead to nerve damage and subsequent neuropathic pain.
-
Infections: Certain infections, such as shingles (herpes zoster), can cause nerve damage and result in neuropathic.
-
Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like multiple sclerosis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the nervous system and lead to pain.
-
Chemotherapy: Some cancer treatments can cause peripheral neuropathy, resulting in pain and discomfort.
-
Alcoholism: Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to nutritional deficiencies and nerve damage, contributing to pain.
2. Symptoms of Neuropathic Pain
The symptoms of neuropathic pain can vary widely among individuals but often include:
-
Burning Sensation: Many people describe neuropathic pain as a burning or tingling sensation, often in the hands or feet.
-
Numbness: Affected individuals may experience numbness or a loss of sensation in the affected areas.
-
Sharp, Stabbing Pain: Some may feel sharp, shooting pains that can be sudden and intense.
-
Hypersensitivity: Neuropathic can lead to allodynia, where even light touch or pressure can cause significant pain.
-
Muscle Weakness: In some cases, neuropathic can be accompanied by muscle weakness or coordination problems.
3. Effective Treatments for Neuropathic Pain
Managing neuropathic pain often requires a multifaceted approach, including:
-
Medications:
- Pregabalin: Pregabalin, commonly prescribed at a dosage of 150 mg, is an anticonvulsant medication that is effective in treating neuropathic pain. It works by inhibiting the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain signaling, thereby reducing the perception of pain. Pregabalin can help alleviate symptoms of diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and other pain conditions.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as amitriptyline and duloxetine, can help alleviate neuropathic by modulating pain signals in the brain.
- Topical Treatments: Creams or patches containing lidocaine or capsaicin can provide localized relief.
-
Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can help improve mobility, strength, and function, which may alleviate some pain symptoms.
-
Psychological Support: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other psychological interventions can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of chronic pain.
-
Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic care may provide additional relief for some individuals.
-
Interventional Procedures: In severe cases, procedures such as nerve blocks or spinal cord stimulation may be considered.
4. The Role of Pregabalin in Neuropathic Pain Management
Pregabalin is a cornerstone in the treatment of neuropathic due to its effectiveness and relatively favorable side effect profile:
-
Mechanism of Action: Pregabalin binds to calcium channels in the nervous system, reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. This action helps to dampen the pain signals sent to the brain.
-
Dosage and Administration: Pregabalin is typically started at a lower dose and gradually increased to 150 mg or higher, depending on the individual’s response and tolerance. It is usually taken orally, with or without food.
-
Side Effects: Common side effects of pregabalin may include dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, and weight gain. Most side effects are manageable, but patients should discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
-
Efficacy: Clinical studies have shown that pregabalin can significantly reduce levels and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from neuropathic.
5. Conclusion
Neuropathic is a challenging condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding its causes and symptoms is crucial for effective management. A combination of medications, including pregabalin at a dosage of 150 mg, physical therapy, psychological support, and alternative therapies can help alleviate pain and improve function. Pregabalin plays a vital role in managing pain due to its mechanism of action and efficacy in reducing pain levels. As always, individuals should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and circumstances.