Introduction
Mushroom cultivation has gained popularity due to the rising demand for fresh, organic produce and the growing recognition of mushrooms’ nutritional and medicinal benefits. Whether for personal consumption or commercial farming, cultivating mushrooms can be a rewarding and profitable venture. This guide explores various aspects of mushroom cultivation, including types of mushrooms, growing techniques, necessary equipment, and best practices for success.
Types of Mushrooms for Cultivation
1. Button Mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus)
- Most commonly consumed mushroom worldwide.
- Requires composted manure and controlled humidity.
2. Oyster Mushrooms (Pleurotus spp.)
- Easy to grow and adaptable to various substrates.
- Ideal for beginners due to their rapid growth.
3. Shiitake Mushrooms (Lentinula edodes)
- Popular for their rich flavor and medicinal properties.
- Grown on hardwood logs or sawdust blocks.
4. Lion’s Mane (Hericium erinaceus)
- Valued for cognitive and neurological benefits.
- Requires humid conditions for optimal growth.
5. Reishi Mushrooms (Ganoderma lucidum)
- Known for their medicinal benefits in traditional medicine.
- Slow-growing but highly profitable in niche markets.
Growing Methods
1. Indoor Cultivation
- Requires climate-controlled environments.
- Ideal for year-round production with minimal contamination risks.
2. Outdoor Cultivation
- Uses natural logs or beds for mushroom growth.
- Suitable for seasonal farming and large-scale production.
3. Hydroponic Cultivation
- Grown in nutrient-rich solutions without soil.
- Allows precise control over nutrients and moisture levels.
4. Organic Cultivation
- Uses natural compost and eco-friendly practices.
- Appeals to health-conscious consumers and specialty markets.
Steps for Successful Mushroom Cultivation
1. Selecting the Right Substrate
- Common substrates: straw, sawdust, coffee grounds, and compost.
- Substrate preparation involves sterilization or pasteurization to eliminate contaminants.
2. Inoculation with Mushroom Spawn
- Spawn serves as the seed for mushrooms.
- Spread evenly in the prepared substrate for effective colonization.
3. Incubation and Colonization
- Maintain optimal temperature and humidity for mycelium growth.
- Ensure darkness or minimal light exposure during this stage.
4. Fruiting Conditions
- Control temperature, humidity, and fresh air exchange.
- Introduce light exposure to stimulate mushroom formation.
5. Harvesting and Storage
- Harvest when mushrooms reach the desired size and cap shape.
- Store in a cool, humid environment to maintain freshness.
Equipment Needed for Mushroom Cultivation
1. Growing Containers
- Bags, trays, or buckets for substrate containment.
2. Sterilization Tools
- Pressure cookers or pasteurization tanks to prevent contamination.
3. Humidity and Temperature Control
- Misting systems and fans to regulate environmental conditions.
4. Lighting System
- Low-intensity LED lights for specific mushroom varieties.
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Contamination Issues
- Maintain hygiene and proper sterilization techniques.
- Use HEPA filters and clean water sources.
2. Inconsistent Growth
- Ensure optimal humidity and temperature control.
- Regularly monitor CO₂ levels and fresh air exchange.
3. Pest Infestations
- Implement natural pest control measures like neem oil and proper ventilation.
Economic Opportunities in Mushroom Farming
- Home-Based Business: Small-scale cultivation for local markets.
- Commercial Farming: Large-scale operations for restaurants and supermarkets.
- Medicinal Mushroom Production: Growing high-value varieties for health supplements.
- Mushroom-Based Products: Developing value-added products like dried mushrooms, powders, and extracts.
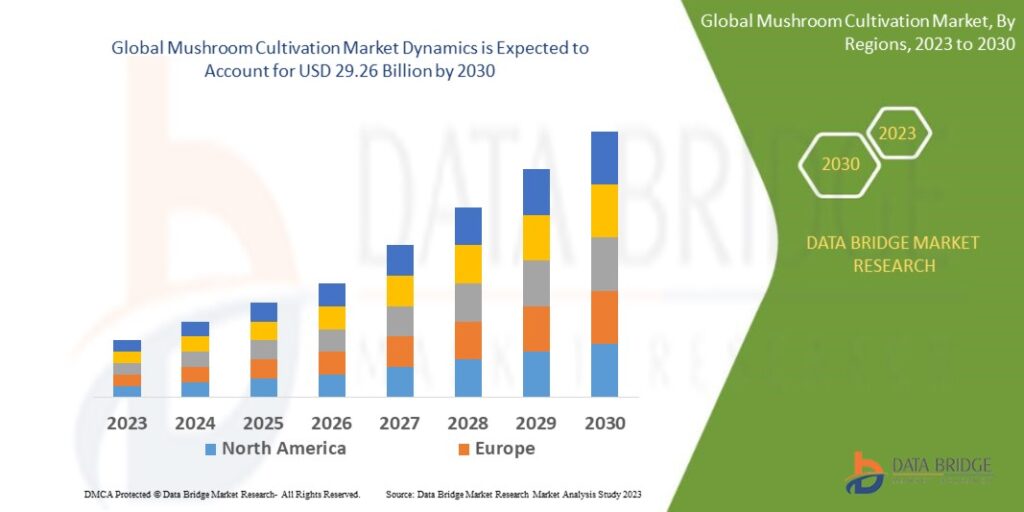
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-mushroom-cultivation-market
Conclusion
Mushroom cultivation is a sustainable and profitable agricultural practice that requires careful planning, proper techniques, and continuous learning. By selecting the right mushroom variety, optimizing growing conditions, and following best practices, both beginners and seasoned growers can achieve success in mushroom farming.