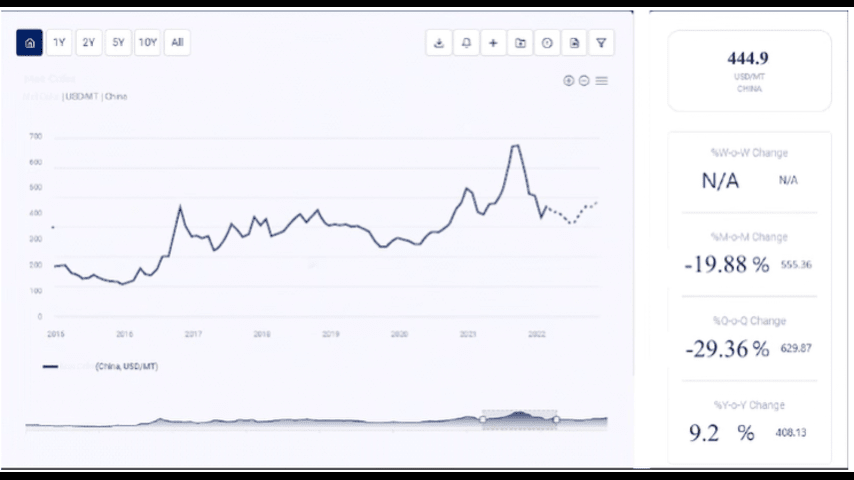
Cocoa is a vital commodity in the global agricultural market, serving as the primary ingredient in chocolate production, confectionery, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. The fluctuation in cocoa prices significantly impacts farmers, traders, manufacturers, and consumers worldwide. Understanding Cocoa Prices Forecast is essential for industry stakeholders to anticipate market shifts and adjust business strategies accordingly.
This article explores the historical trends, key price drivers, regional market analysis, and future forecasts for cocoa prices, providing valuable insights for producers, investors, and policymakers.
1. Overview of the Cocoa Market
1.1 Applications of Cocoa
Cocoa is widely used in:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Chocolate, cocoa powder, dairy products, and bakery goods.
- Cosmetic Industry: Skin care products, lotions, and creams containing cocoa butter.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in health supplements and medicinal formulations.
- Functional Foods: Growing demand for dark chocolate and organic cocoa products for health benefits.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/cocoa-price-trends/pricerequest
1.2 Market Growth and Trends
- Rising Chocolate Consumption: Increasing demand for premium and organic chocolates globally.
- Health Benefits Awareness: Consumers preferring dark chocolate due to its antioxidants and flavonoids.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Ethical sourcing, Fair Trade cocoa, and Rainforest Alliance-certified cocoa gaining popularity.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Climate change and geopolitical factors impacting cocoa production.
2. Historical Cocoa Price Trends
2.1 Early 2000s – Market Stability and Steady Demand
- Cocoa prices remained relatively stable, driven by consistent production in West Africa (Ghana, Ivory Coast, Nigeria).
- Europe and North America were the largest consumers, while Asia-Pacific demand started growing.
2.2 2008-2009 – Global Financial Crisis and Demand Fluctuations
- The economic downturn led to a temporary decline in cocoa demand.
- Prices fluctuated due to reduced consumer spending on luxury goods like chocolate.
2.3 2010-2019 – Supply Chain Issues and Market Volatility
- Cocoa price spikes were observed due to pest infestations and diseases affecting cocoa trees.
- Political instability in Ivory Coast and Ghana led to temporary supply disruptions.
- Increasing demand from China and India contributed to steady price growth.
2.4 2020-2022 – COVID-19 Pandemic and Market Uncertainty
- Chocolate sales dropped temporarily due to lower tourism and hospitality demand.
- Supply chain issues delayed shipments, impacting cocoa availability.
- Prices rebounded as demand for at-home chocolate consumption increased.
2.5 2023-Present – Climate Change and Inflation Pressures
- Unfavorable weather conditions (El Niño effects) caused reduced cocoa yields.
- Inflationary pressures raised production and transport costs, affecting cocoa prices.
- Sustainability concerns and ethical farming practices influenced market demand.
3. Key Factors Influencing Cocoa Prices
3.1 Weather Conditions and Climate Change
- Cocoa trees are highly sensitive to temperature and rainfall fluctuations.
- Climate issues like El Niño, droughts, and excessive rainfall reduce production yields.
- Deforestation policies and reforestation efforts impact land availability for cocoa farming.
3.2 Supply and Production Challenges
- West Africa accounts for nearly 70% of global cocoa production.
- Any disruptions in Ghana, Ivory Coast, or Nigeria directly affect global cocoa prices.
- Aging cocoa plantations with low-yield trees contribute to supply limitations.
3.3 Labour Costs and Farming Practices
- Child labor concerns and fair trade regulations impact cocoa production costs.
- Government policies on minimum wages for cocoa farmers influence price trends.
- Mechanization and technology adoption are improving yield efficiency.
3.4 Global Demand and Consumer Preferences
- Increased demand for premium chocolates (organic, dark, sugar-free).
- Expansion of cocoa-based functional foods driving market growth.
- Growing middle-class population in Asia-Pacific boosting demand.
3.5 Trade Policies, Import-Export Regulations, and Currency Exchange Rates
- Government subsidies and tariffs influence international cocoa trade.
- Currency fluctuations between the U.S. dollar and cocoa-producing country currencies impact prices.
- Export taxes in Ghana and Ivory Coast affect cocoa supply costs.
4. Regional Cocoa Market Trends
4.1 West Africa – The Cocoa Production Hub
- Ivory Coast and Ghana lead global cocoa production.
- Political instability and climate change impact crop yields.
- Governments implementing cocoa price stabilization policies to protect farmers.
4.2 Europe – Largest Chocolate Consumer
- Germany, Switzerland, Belgium, and the UK are major cocoa importers.
- Increasing demand for ethically sourced and organic cocoa.
- EU regulations on sustainable sourcing shaping supply chains.
4.3 North America – Innovation-Driven Market
- The U.S. is a leading chocolate consumer and cocoa importer.
- Rising preference for low-sugar and vegan chocolate alternatives.
- Fair-trade and sustainable cocoa sourcing gaining importance.
4.4 Asia-Pacific – Emerging Growth Region
- China and India experiencing increased chocolate consumption.
- Japan and South Korea leading in premium and dark chocolate segments.
- Expansion of domestic cocoa processing industries in Southeast Asia.
5. Future Cocoa Price Forecast (2024-2030)
5.1 Short-Term Forecast (2024-2025)
- Weather-related supply issues will keep prices volatile.
- Stable demand from Europe and North America, with stronger growth in Asia-Pacific.
- Fair-trade and ethical sourcing initiatives will slightly increase production costs.
5.2 Mid-Term Forecast (2026-2028)
- Expansion of sustainable cocoa farming practices will help stabilize supply.
- Rising energy and logistics costs may contribute to moderate price increases.
- Growth in functional food and nutraceutical markets will support higher cocoa demand.
5.3 Long-Term Forecast (2029-2030)
- Climate adaptation strategies and new farming techniques could improve yields.
- Increased adoption of alternative cocoa sources (lab-grown cocoa, synthetic chocolate) may impact prices.
- Cocoa-growing countries investing in value-added processing to reduce raw cocoa exports and increase profitability.
Cocoa prices are influenced by weather conditions, geopolitical factors, labor costs, trade policies, and shifting consumer preferences. While short-term fluctuations are expected due to supply constraints and climate change, the long-term market outlook remains positive, with sustainable farming practices, growing chocolate demand, and expanding food applications driving price trends.
Industry stakeholders must focus on supply chain resilience, ethical sourcing, and technological innovations to navigate price volatility and ensure sustainable growth in the global cocoa market.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: [email protected]
Toll-Free Numbers:
- USA & Canada: +1 307 363 1045
- UK: +44 7537171117
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Last Update: January 30, 2025