Introduction
The algae biofuel market is gaining traction as the world urgently seeks sustainable and renewable alternatives to fossil fuels. Algae, a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms, can produce oils that are convertible into biodiesel, jet fuel, and other biofuels. Unlike traditional crops used for biofuel, algae can be cultivated in non-arable areas, require minimal freshwater, and can absorb CO₂ during growth — making it a promising solution in the fight against climate change.
This article explores the current state of the algae biofuel market, its growth drivers, technological developments, regional trends, and the challenges that lie ahead.
Market Overview
Algae biofuels have moved from the lab to pilot and commercial scales over the last two decades. While the market is still in its early stages compared to other renewable energy sectors, it holds significant promise due to algae’s high productivity, rapid growth rate, and versatility.
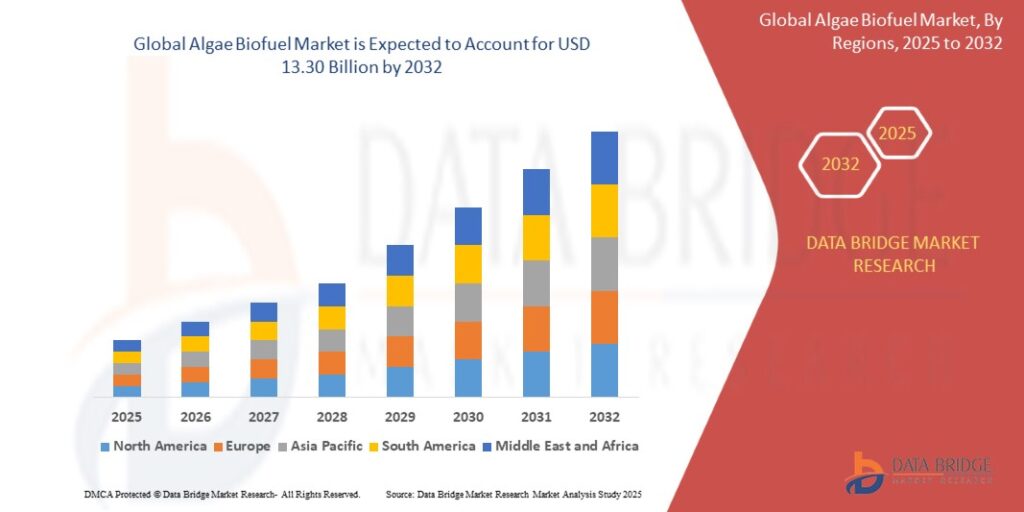
As of 2024, the global algae biofuel market is valued at approximately USD 9–10 billion, and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7% to 10% over the next decade. Major investments from governments, energy companies, and environmental organizations are fueling innovation and commercial deployment.
Key Growth Drivers
1. Environmental Sustainability
Algae biofuels offer a carbon-neutral alternative to fossil fuels. Algae can absorb more CO₂ per acre than forests, and they can be cultivated using wastewater or seawater, reducing the strain on freshwater resources.
2. High Yield and Productivity
Algae can yield up to 20 times more oil per acre than traditional crops like corn or soybeans. They grow faster and can be harvested daily, which dramatically improves production efficiency.
3. Diverse Applications
Beyond transportation fuels like biodiesel and aviation fuel, algae can also produce bioethanol, biogas, and even serve as feedstock for bioplastics, cosmetics, and nutraceuticals, adding to their economic viability.
4. Government Incentives
Countries across North America, Europe, and Asia are supporting algae biofuel development through research grants, subsidies, and tax incentives as part of their broader clean energy transition goals.
Technology Landscape
Technological innovations are driving down production costs and improving the efficiency of algae biofuel production. Key technological areas include:
– Cultivation Systems
Two main systems are used:
-
Open Pond Systems: Cost-effective but vulnerable to contamination and environmental fluctuations.
-
Closed Photobioreactors (PBRs): More expensive but offer controlled conditions, higher yields, and scalability.
– Harvesting and Extraction
Techniques such as centrifugation, filtration, and flocculation are used to separate algae biomass. Oil extraction is often done through mechanical pressing or solvent extraction. Recent advancements focus on non-destructive extraction methods that allow continuous production.
– Conversion to Biofuel
Lipid transesterification is the primary process to convert algae oil to biodiesel. Algae can also undergo pyrolysis, gasification, or hydrothermal liquefaction to produce other fuel types.
Regional Insights
– North America
The U.S. leads in research and commercialization, with support from the Department of Energy (DOE) and organizations like the Algae Biomass Organization. Multiple startups and universities are exploring scalable algae biofuel solutions, especially for aviation.
– Europe
Europe emphasizes sustainable energy and circular economies. Countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and the UK are investing in algae-based biofuels as part of their renewable energy strategies, often combining algae cultivation with wastewater treatment.
– Asia-Pacific
Asia is a hotspot for algae cultivation due to favorable climate conditions. Countries like China, India, and Japan are investing in algae farms and integrated bio-refineries. India, in particular, is targeting algae biofuel as part of its rural energy and clean fuel initiatives.
– Rest of the World
In regions like Latin America and the Middle East, algae biofuel initiatives are emerging, often integrated with aquaculture and wastewater treatment projects.
Competitive Landscape
The algae biofuel market includes a mix of startups, research institutions, and large energy corporations. Key players include:
-
Sapphire Energy (U.S.)
-
Algenol Biotech (U.S.)
-
Solazyme (now TerraVia, U.S.)
-
ExxonMobil (R&D partnerships in algae biofuel)
-
Neste (Finland – exploring algae feedstocks for biodiesel)
Collaborations between academic institutions and commercial players are accelerating progress, particularly in scaling up production and improving cost-efficiency.
Challenges Facing the Market
Despite its promise, the algae biofuel industry faces several hurdles:
– High Production Costs
Compared to fossil fuels and even other biofuels, algae biofuel is still expensive to produce. Costs for cultivation, harvesting, and extraction remain a major bottleneck.
– Scale-Up Difficulties
Transitioning from lab or pilot-scale production to commercial-scale deployment is technically and economically challenging, particularly when maintaining quality and yield.
– Market Competition
Algae biofuel competes with other renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and electric vehicles. Additionally, traditional biofuels made from crops are still more cost-effective in many regions.
– Regulatory Hurdles
Inconsistent policies and regulatory uncertainty can deter long-term investments. Approval for use in transportation, particularly aviation, also involves strict safety standards.
Future Outlook
The algae biofuel market is poised for significant growth over the next decade, particularly as the world moves aggressively toward carbon neutrality. Some of the most promising developments on the horizon include:
-
Integration with Carbon Capture: Using algae to absorb emissions from industrial plants and convert them into usable fuel.
-
Genetically Engineered Algae: Enhanced strains that offer higher oil content, faster growth, and better resistance to contamination.
-
Hybrid Bio-Refineries: Facilities that co-produce fuels, food supplements, and bio-based materials to improve economic feasibility.
-
Military and Aviation Use: The U.S. military and commercial airlines are testing algae-based jet fuels, which could significantly drive demand if widely adopted.
Conclusion
The algae biofuel market represents a unique intersection of energy innovation, environmental sustainability, and biotechnology. Although the industry faces technical and economic challenges, ongoing research, supportive policies, and growing environmental urgency are pushing it closer to large-scale viability.
With a broad range of applications, high productivity potential, and ecological benefits, algae biofuel may play a pivotal role in the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Get more Details
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-algae-biofuel-market