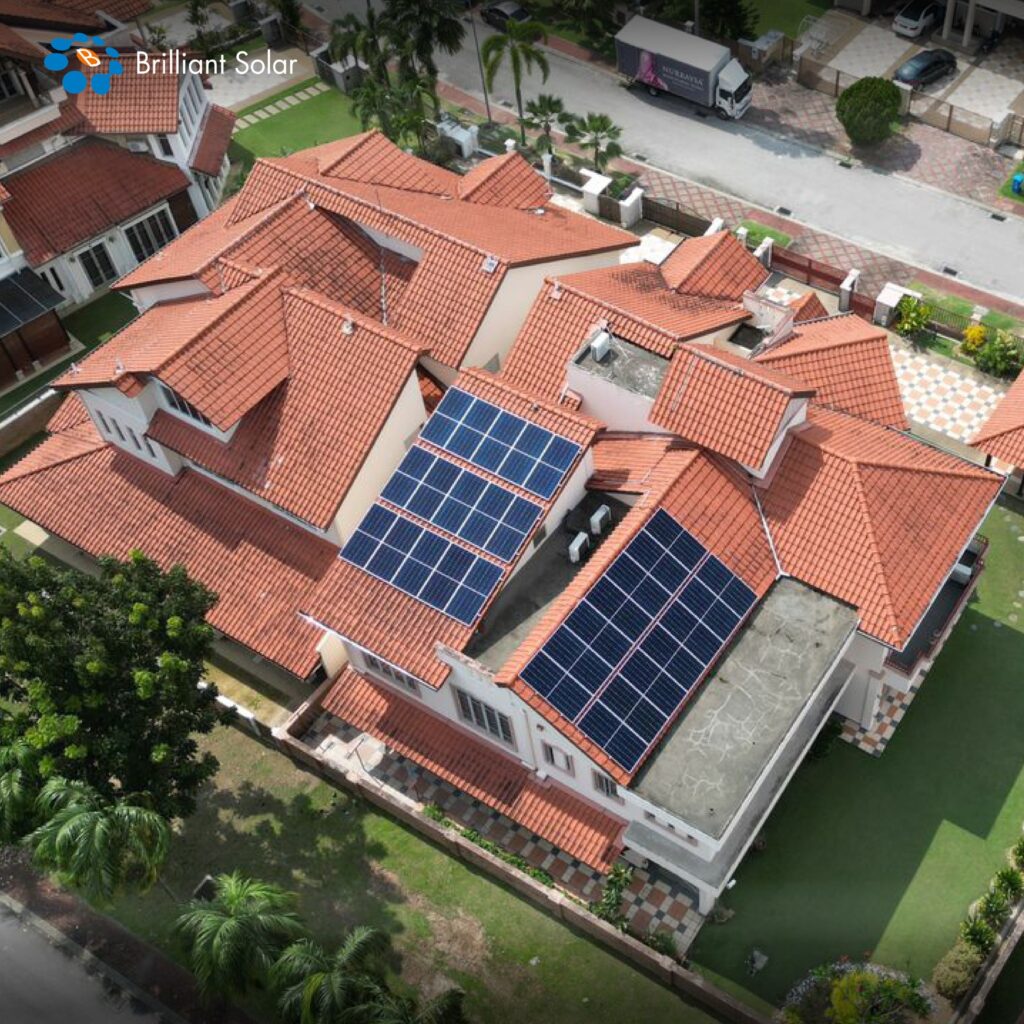
Solar power is working towards redefining the global energy landscape. Inherently absolutely clean and renewable, the source of energy exploits sunlight in generating electricity for a much more sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. This shift towards renewable energy is by necessity if one is to reduce carbon emissions and fight climate change. Malaysia, abounding with so much sunlight, holds immense potential for this technology.
The increasing adoption of solar power within Malaysia underlines how serious the nation is towards achieving sustainable development. In that case, government policies and incentives imperative in promoting the use of solar energy. All of these are complimentary initiatives geared toward energy mix diversification with an ultimate focus on rendering redundant the sources of non-renewable energy.
It is very key to understand the mechanics that surround solar power, its benefits, and the various challenges it faces, if further adoption is to be encouraged. Other than considerable environmental benefits, solar power also has significant cost savings and improved energy security. This blog considers the growth of solar power in Malaysia by among other things looking at the accrued benefits against the challenges that have to be overcome. It is intended to give insight into what can be expected of the prospect and future with regard to solar energy in Malaysia.
Understanding Solar Power
What is Solar Power?
Solar power uses sunlight to generate electricity. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy. This process is clean and sustainable. Solar power is becoming more popular worldwide.
How Solar Power Works
Solar panels contain cells made of silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it creates an electric current. This current is then converted into usable electricity. Solar power systems can be installed on rooftops or open land.
Different Types of Solar Panels
There are several types of solar panels. The most common types are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film solar panels.
- Monocrystalline panels are the most efficient. They are made from a single crystal structure.
- Polycrystalline panels are less expensive but slightly less efficient. They are made from multiple crystal structures.
- Thin-film panels are the least efficient but are flexible and lightweight. They are ideal for certain applications.
The Rise of Solar Power in Malaysia
Growth of Solar Power Usage in Malaysia
Solar power usage in Malaysia has grown rapidly. This growth is due to the country’s commitment to renewable energy. The Malaysian government has set ambitious targets for solar energy. It aims to increase the share of renewable energy in the national energy mix.
Government Policies Supporting Solar Energy
The Malaysian government very much supports solar energy through various policies and initiatives. One of these policies is including a Feed-in Tariff program. The adoption of renewable energy is encouraged with the incentives given on the production thereof. This means that solar power producers are guaranteed a payment for electricity production, therefore variously luring many investors’ and developers’ interest into the industry of solar.
Key Players in the Malaysian Solar Market
Several key players drive the solar market in Malaysia. These include government agencies, private companies, and non-governmental organizations. Major solar energy companies in Malaysia include Cypark Resources, Solarvest Holdings, and Plus Solar. These companies develop and install solar power systems across the country. They play a crucial role in promoting the use of solar energy.
Benefits of Solar Power
Environmental Benefits
Many are the environmental benefits that come with solar power. It minimizes overreliance on fossil fuel, which forms the bulk of greenhouse gas emissions. Through that, Malaysia will manage to reduce its carbon footprint. Solar energy is clean; it does not emit dangerous fumes. It improves air quality by reducing pollution.
Cost Savings for Households and Businesses
Solar power offers extreme cost savings. When installed, solar panels give free electricity. Therefore, due to this fact, it reduces energy bills for households and businesses. The amount invested in the installation of solar panels can normally be returned within a few years. After recovering the invested amount, the savings from electricity bills can be huge. Moreover, the government offers various incentives and tax benefits for the installation of solar power systems. This further slashes the overall cost.
Energy Independence and Security
Solar power increases energy independence and security. By generating electricity locally, Malaysia can reduce its dependence on imported energy. This is important for ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply. Solar power also provides energy security in remote areas. It can bring electricity to regions not connected to the national grid. This improves the quality of life for people in rural areas.
Job Creation and Economic Growth
The solar power industry creates jobs and stimulates economic growth. The installation, maintenance, and manufacturing of solar panels create employment opportunities. This benefits local communities and contributes to the economy. As the solar industry grows, it attracts investments and fosters innovation. This can lead to the development of new technologies and business opportunities.
Scalability and Flexibility
Solar power systems are scalable and flexible. They can be installed on a small scale, such as on residential rooftops, or on a large scale, such as solar farms. This makes solar power suitable for a wide range of applications. Solar panels can also be installed in various locations, including urban and rural areas. This flexibility allows for the efficient use of available space and resources.
Government Initiatives and Policies
Overview of Current Policies
The Malaysian government has implemented various policies to promote solar power. The Feed-in Tariff (FiT) program is one of the key initiatives. It guarantees payments to solar power producers for the electricity they generate. This encourages investment in solar energy. Another important policy is the Net Energy Metering (NEM) scheme. This allows consumers to offset their electricity bills by exporting excess solar energy back to the grid. These policies make solar power more attractive and financially viable.
Incentives and Subsidies for Solar Energy
Incentives and subsidies play a crucial role in promoting solar power. The government offers tax incentives for the installation of solar panels. These incentives reduce the overall cost of solar systems. Additionally, there are grants and loans available for solar power projects. These financial aids make it easier for households and businesses to invest in solar energy. It is important to research and take advantage of these opportunities.
Future Plans and Targets for Solar Power
The Malaysian government has set ambitious targets for the future of solar power. By 2025, it aims to have 20% of the country’s electricity generated from renewable sources. This includes a significant contribution from solar energy. To achieve this goal, the government plans to implement more supportive policies and programs. It also aims to attract more investments in the solar sector. These plans and targets indicate a strong commitment to expanding solar power in Malaysia.
How Solar Power is Transforming Communities
Solar Power’s Impact on Rural Areas
Solar power is making a significant impact on rural areas in Malaysia. Many rural regions are not connected to the national grid. Solar power provides a reliable and sustainable energy source for these areas. It enhances the quality of life by providing electricity for lighting, heating, and other essential needs. This is particularly important for remote villages and communities.
Enhancing Energy Access and Quality of Life
Solar power improves energy access and the quality of life. It enables the use of electrical appliances and modern technologies. This can lead to better education and healthcare services in rural areas. For instance, solar-powered lights allow children to study at night. Solar energy also powers medical equipment in rural clinics. These improvements contribute to the overall development of rural communities.
Examples of Community Solar Projects
Several community solar projects have been successful in Malaysia. These projects involve the installation of solar panels in rural areas. They provide electricity to multiple households or community facilities. One example is the Solar Home System (SHS) program. It provides solar power systems to remote villages. These projects demonstrate the potential of solar power to transform communities. They serve as models for future initiatives.
The Future of Solar Power in Malaysia
Predicted Growth and Trends
The future of solar power in Malaysia looks promising. The solar market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Advances in technology will make solar panels more efficient and affordable. This will drive the adoption of solar power across the country. The government’s commitment to renewable energy will also support this growth. Additionally, the increasing awareness of environmental issues will encourage more people to switch to solar power.
Technological Advancements in Solar Energy
Technological advancements are shaping the future of solar energy. New materials and designs are improving the efficiency of solar panels. Innovations like bifacial panels and solar tracking systems are enhancing energy capture. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, are becoming more advanced. This allows for better storage and use of solar energy. These advancements will make solar power more efficient and reliable.
Potential for Job Creation and Economic Benefits
The growth of the solar industry will create jobs and boost the economy. The installation and maintenance of solar systems require skilled labor. This will create employment opportunities in various sectors. The manufacturing of solar panels and related equipment will also contribute to economic growth. Furthermore, the adoption of solar power will reduce energy costs for businesses. This will enhance their competitiveness and contribute to economic development.
Conclusion
One of the salient features of Malaysia’s renewable energy strategy has been solar power. Inherence in it brings advantages with respect to the environment, monetary savings, and security based on its source. Notwithstanding, the existing challenges, the growth in solar power is paved with very supportive government policies and other initiatives. Solar energy introduces transformation in issues related to access to energy and improvement in the quality of life in communities. Increasing investment and continuous technological changes ensure a prospective future for solar power in Malaysia. Embracing solar will help jumpstart the clear pathway for a green, sustainable future for the country.